Data Governance
Data governance is an important link in work to build an enterprise big data platform. Only by establishing a complete data governance system and ensuring the quality of data content can the enterprise truly and effectively explore the data value within the enterprise and improve its competitiveness externally.
- Understand the business and technical strategies and objectives of the enterprise in the near and medium term, especially the information related to data governance.
- Through written interviews, field research and other means to create a data governance atmosphere within the enterprise, so that the data governance goals of relevant personnel are shared.
- Make plans based on realistic gaps and develop data planning for your business over the next 3-5 years.
Data Governance Background
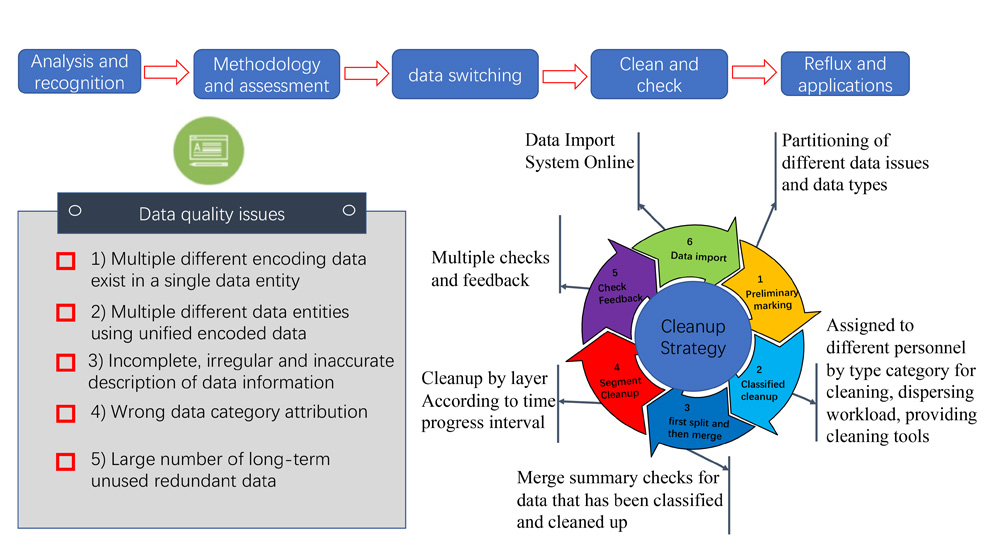
Data is unknown: users do not know what data is in the big data platform, and do not know what the relationship between these data and business is. Although people are aware of the importance of big data, but there is no key data in the platform to solve the business problems they face? Where to look for the data?
Data uncontrollable: Uncontrollable data is a problem that has been around since the traditional data platform, and it is more obvious in the age of big data. The absence of uniform data standards makes data difficult to integrate and unify, and the absence of quality control results in massive amounts of data being difficult to exploit because of their low quality, without any management process to effectively manage the entire big data platform.
Data is unobtainable: even if users know what data they need for their business, they do not have easy self-service access to the data, resulting in a long development process before the data acquisition, which makes it difficult for business analysis to be met quickly. However, in the age of big data, the business demands a rapid analysis of business problems, and such long response time is difficult to meet business needs.
Data is not connected: In the age of big data, enterprises have a large amount of data, but the correlation between enterprise data knowledge is still relatively weak, without linking data and knowledge system. Enterprise employees are difficult to achieve the rapid conversion between data and knowledge, and can not explore and mine the data by themselves, which leads to the deep value of data difficult to be revealed.
Data uncontrollable: Uncontrollable data is a problem that has been around since the traditional data platform, and it is more obvious in the age of big data. The absence of uniform data standards makes data difficult to integrate and unify, and the absence of quality control results in massive amounts of data being difficult to exploit because of their low quality, without any management process to effectively manage the entire big data platform.
Data is unobtainable: even if users know what data they need for their business, they do not have easy self-service access to the data, resulting in a long development process before the data acquisition, which makes it difficult for business analysis to be met quickly. However, in the age of big data, the business demands a rapid analysis of business problems, and such long response time is difficult to meet business needs.
Data is not connected: In the age of big data, enterprises have a large amount of data, but the correlation between enterprise data knowledge is still relatively weak, without linking data and knowledge system. Enterprise employees are difficult to achieve the rapid conversion between data and knowledge, and can not explore and mine the data by themselves, which leads to the deep value of data difficult to be revealed.
Data Governance Methodology
Key Points of Data Governance
Seven elements of data governance
- It's hard to start with everything (build a data management team).
- The management system is the guarantee (develop management method and identify responsibility).
- Overall control (Enterprise data model).
- Book in the same text, car in the same track (Data standards).
- Bridges between business and IT (metadata).
- Common business data is unified first (master data).
- Important guarantee of data value (data quality).
Data Governance Value
Data Standards Establishment
- Establish enterprise data standards;
- Establishment of an information standardization organization;
- Standardized management system and process of supporting information;
- Build data management platform, with supporting tools;
Data Quality Improvement
- Data quality definition
- Develop data quality management standards based on business requirements;
- Develop quality measurement indicators for multiple dimensions such as accuracy,completeness, consistency, validity and uniqueness of data;
- Data quality monitoring
- Set up data quality detection points in the flow of data;
-
Continuous feedback, tracking, reporting and repair of data quality, in order to achieve the goal of continuous improvement of data quality;
Data Value Utilization
- Efficient data sharing, comprehensive integration, improve business efficiency;
- Accurate statistics and analysis to support accurate decision making;
- Increase IT development flexibility and reduce system integration costs